9 Common Childhood Injuries That Need Urgent Medical Attention
Recognize signs that require urgent care in children.
Children are naturally curious and energetic, often leading to bumps, scrapes, and falls. While many minor injuries can be treated at home, some require immediate medical attention to prevent complications. Recognizing the signs of serious injuries ensures timely intervention and better outcomes. Parents and caregivers should know these critical situations to safeguard a child’s health.
Below are nine common childhood injuries that demand urgent medical evaluation:
1. Severe Head Injuries and Concussions
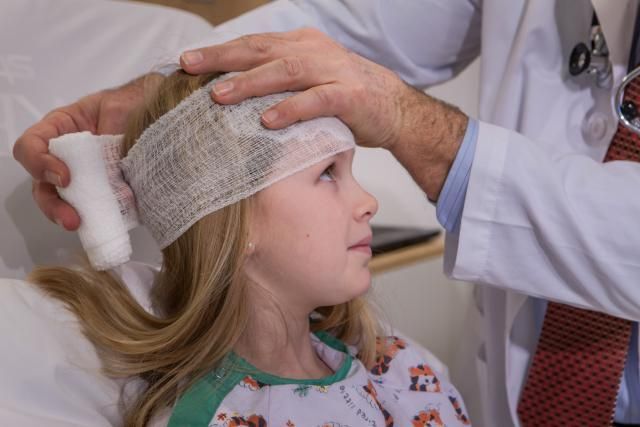
Head injuries are common in active children, but severe impacts can lead to concussions or traumatic brain injuries (TBI). While minor bumps may only need observation, certain symptoms demand immediate medical attention.
Some critical signs that require emergency care include:
- Loss of consciousness: Even brief blackouts after a fall need evaluation.
- Persistent vomiting: More than one or two episodes could indicate brain trauma.
- Confusion or disorientation: This involves the inability to recognize familiar people or places.
- Unequal pupil size: This is a possible sign of brain swelling or nerve damage.
- Seizures or convulsions: This indicates abnormal brain activity post-injury.
- Blood or clear fluid from nose/ears: This suggests a skull fracture or cerebrospinal fluid leak.
- Severe headache or dizziness: This involves worsening pain or balance issues.
- Slurred speech or weakness: This includes delayed neurological symptoms that should never be ignored.
Even if a child appears fine initially, “watch-and-wait” isn’t safe with head injuries—delayed complications can arise hours later. As such, immediate medical evaluation is crucial to prevent long-term damage. Also, for parents looking for expert advice on pediatric care, they may consider consulting with reliable providers like Just 4 Kids in their area.
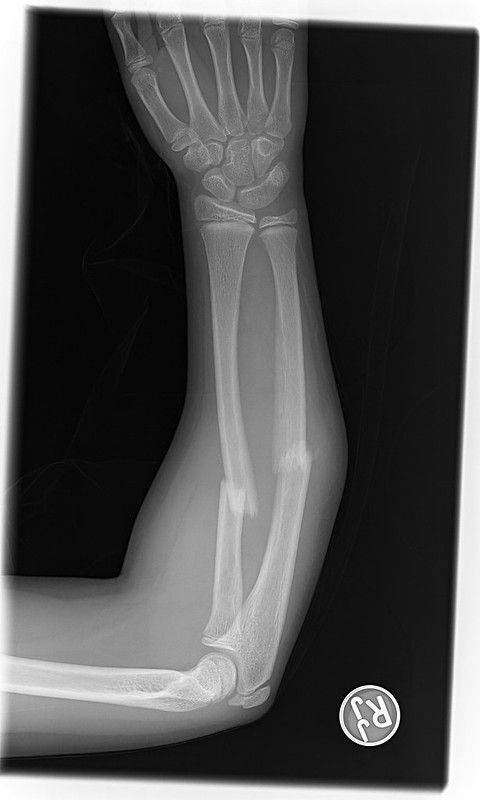
2. Broken Bones and Fractures
Due to their developing structure, children’s bones are more flexible than adults’, but fractures are still common due to falls, sports injuries, or accidents. While some breaks may be minor (like hairline fractures), others require urgent medical care to ensure proper healing.
Some key signs of a possible fracture include:
- Visible deformity: The limb or joint appears bent, crooked, or misaligned.
- Severe swelling or bruising: This involves rapid discoloration (blue, purple, or black) around the injured area.
- Inability to move or bear weight: The child refuses to use the limb due to extreme pain.
- Intense pain when touched or moved: Even gentle pressure can cause significant discomfort.
- Snapping or grinding sound at injury time: A “pop” or crunching noise may indicate a break.
- Numbness or tingling: This suggests possible nerve damage near the fracture site.
If a fracture is suspected, it’s essential to immobilize the area (using a splint or sling) and seek immediate medical attention to prevent complications like improper bone healing. X-rays are also typically needed for an accurate diagnosis.
3. Deep Cuts and Severe Bleeding

Active children often suffer cuts and scrapes, but deep lacerations require immediate medical attention to prevent complications like infection or excessive blood loss. While small wounds can be treated at home with cleaning and bandages, certain signs indicate a need for professional care.
Some critical signs requiring urgent medical attention include:
- Gaping wounds: These are cuts that are wide enough to expose underlying muscle, fat, or bone.
- Uncontrolled bleeding: This involves blood soaking through multiple bandages even after 10+ minutes of firm pressure.
- Deep puncture wounds: These come especially from nails, animal bites, or dirty/rusty objects (high tetanus risk).
- Facial or joint injuries: Cuts near eyes, mouth, or over joints often need specialized closure.
- Signs of infection: These include increasing redness, warmth, swelling, or pus after initial injury.
- Embedded debris: This involves dirt, glass, or other foreign material trapped deep in the wound
Applying steady pressure with a clean cloth and elevating the injured area while seeking emergency care are essential for severe bleeding. Tetanus vaccination status should also be verified for dirty wounds. Stitches or medical glue may be required for proper healing.
4. Burns Requiring Medical Attention

While minor first-degree burns (red skin without blisters) can be treated with cool water and aloe vera, more serious burns require immediate medical intervention to prevent complications and promote proper healing.
Some danger signs requiring emergency treatment include:
- Large blisters or charred skin: This indicates deep second-degree or third-degree burns that damage multiple skin layers.
- Burns covering sensitive areas: These include face, hands, feet, joints, or genitals due to high risk of functional impairment.
- Difficulty breathing: If burn occurred in a fire or enclosed space, it signals potential smoke inhalation.
- White or leathery skin appearance: This is a characteristic of third-degree burns that destroy nerve endings.
- Burns larger than 3 inches: These involve any burn covering a significant portion of the body.
- Electrical or chemical burns: These often cause deeper tissue damage than visible on the surface
For serious burns, it’s crucial to cool the area with room-temperature water (never ice), remove constrictive clothing/jewelry, and cover loosely with sterile gauze while seeking emergency care. Never pop blisters or apply home remedies like butter or toothpaste.
5. Choking and Breathing Difficulties

Choking is a life-threatening emergency where food, small toys, or other objects block a child’s airway, cutting off oxygen supply. While first aid measures like back blows and abdominal thrusts (Heimlich maneuver) can help, persistent obstruction requires emergency intervention.
Some emergency warning signs to watch out for include:
- Silent choking: The child can’t cough, cry, or make noise (complete airway blockage).
- Blue-tinged lips or face: This indicates oxygen deprivation (cyanosis).
- Loss of consciousness: The child collapses from lack of oxygen.
- Weak/ineffective coughing: This involves gasping without clearing the obstruction.
- High-pitched wheezing: This suggests partial blockage still restricting airflow.
When dealing with choking and breathing difficulties, parents should call emergency services if the child shows any danger signs. They should also begin CPR if the child becomes unresponsive.
6. Poisoning and Ingestion of Harmful Substances

Accidental poisoning is a leading cause of childhood emergencies, with common culprits including medications, household cleaners, and toxic plants. Rapid recognition of symptoms can mean the difference between life and death.
Some life-threatening symptoms that require proper care include:
- Labored breathing or choking: This indicates airway compromise or lung irritation.
- Seizures or convulsions: These signal neurological involvement from toxins.
- Sudden drowsiness or unconsciousness: This suggests central nervous system depression.
- Chemical burns: These involve white or red lesions around mouth/lips from corrosive substances.
- Pupil changes: These involve abnormal dilation or constriction.
As part of the emergency response protocol, it’s crucial for parents not to induce vomiting unless directed by professionals. They should also rinse mouth/skin if exposed to corrosive substances, bring container/plant sample to identify the toxin, and monitor breathing/pulse until help arrives.
7. Eye Injuries

Eye injuries in children—whether from scratches, chemicals, or foreign objects—can escalate quickly and risk permanent vision damage if not treated promptly. Immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent complications like corneal ulcers or retinal damage.
Some emergency warning signs include:
- Severe or persistent pain: This involves discomfort that doesn’t improve with rinsing.
- Sudden vision changes: These include blurriness, double vision, or light sensitivity.
- Visible blood in the eye: This involves subconjunctival hemorrhage or deeper bleeding.
- Chemical exposure: This involves burns from cleaners, solvents, or aerosols.
- Embedded foreign object: This includes debris stuck on the cornea or under the eyelid.
- Swelling or bruising: This involves after blunt trauma (e.g., sports injury).
Furthermore, it’s essential to know that even seemingly minor eye injuries warrant an ophthalmologist’s evaluation to rule out hidden damage. Delayed treatment risks infection or scarring.
8. High-Impact Sports Injuries

High-impact sports collisions can lead to serious injuries that aren’t always immediately apparent. While bruises and minor sprains are common, certain symptoms indicate potentially life-threatening damage requiring urgent medical intervention.
Some critical danger signs to watch out for include:
- Inability to bear weight on injured limbs: This suggests fractures or severe ligament damage.
- Abdominal pain with vomiting: This may indicate internal bleeding or organ injury.
- Neck or spine pain: This may be a potential spinal cord involvement.
- Severe headache with confusion: This involves a possible concussion or brain injury.
To address these common injuries properly, it’s important to immobilize injured areas, especially the head and neck, apply ice to reduce swelling except open fractures, and seek immediate medical attention for any danger signs. Parents should also monitor for delayed symptoms. Lastly, they should never allow a child to “shake off” or continue playing after exhibiting these warning signs, as this may exacerbate pediatric injuries.
9. Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis)
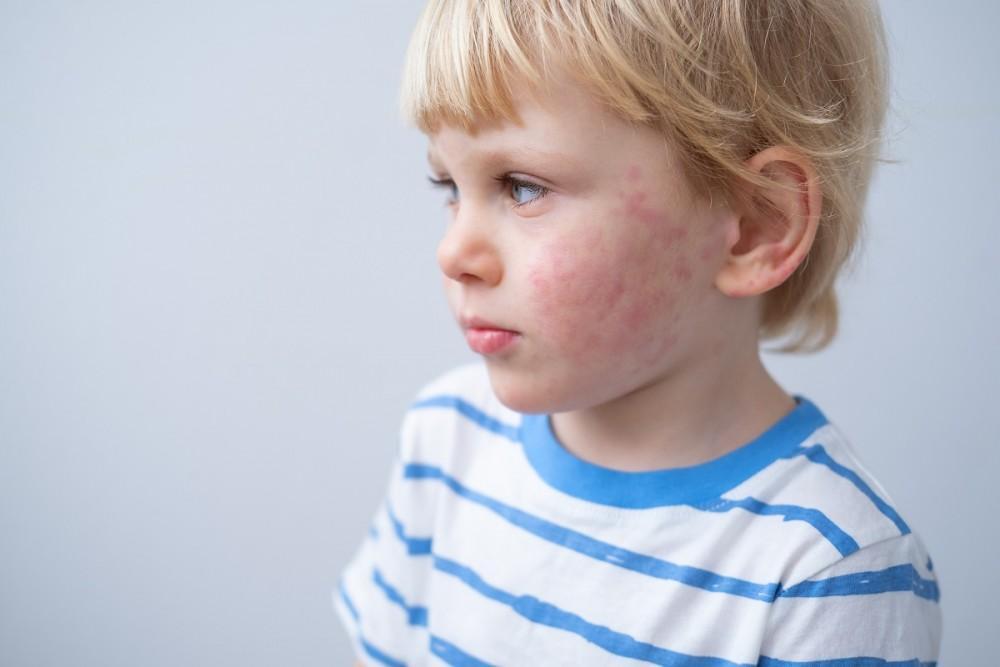
Anaphylaxis is a severe, whole-body allergic reaction that progresses rapidly and can be fatal without immediate treatment. Common triggers include peanuts, shellfish, insect stings, and certain medications.
Also, below are the critical emergency symptoms to be wary of:
- Facial/throat swelling: This usually happens in the lips, tongue, or uvula.
- Breathing difficulties: These include wheezing, stridor (high-pitched breathing), or chest tightness.
- Rapid, weak pulse: This is a sign of impending circulatory collapse.
- Sudden fainting/dizziness: This is caused by dangerous blood pressure drop.
- Hives with vomiting: This involves widespread rash combined with gastrointestinal distress.
- Confusion or slurred speech: This indicates oxygen deprivation.
When a child experiences allergic reactions, it’s essential for the parents to administer epinephrine immediately if available and lie the child flat. If breathing is difficult, then keep upright. Parents should also be prepared to perform CPR and avoid oral medications or food that could worsen throat swelling.
Lastly, children with known severe allergies should always carry two epinephrine auto-injectors. Second count - delayed treatment increases mortality risk. All anaphylaxis cases require emergency room evaluation due to potential biphasic reactions.
Conclusion
While minor injuries are part of childhood, certain conditions require urgent medical treatment. Parents should stay vigilant and seek professional help when necessary. By keeping the information mentioned above in mind, parents can ensure children receive the best possible care.