Fungal Acne: Causes and Treatments That Work
Treat and prevent fungal acne with these effective skincare solutions.
Dealing with fungal acne can feel overwhelming. It’s often mistaken for regular acne, but it’s not the same. This skin condition is caused by yeast overgrowth in hair follicles. Unlike regular acne, fungal acne appears as small, itchy bumps and doesn’t respond to standard acne treatments. Learning how to identify and treat fungal acne is important for healthy skin.
What is Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis, is caused by an overgrowth of yeast. This yeast lives on everyone’s skin but grows too much under certain conditions. The result is small, uniform bumps that may feel itchy. It often shows up on the chest, back, shoulders, and sometimes the face.
This type of acne can look like regular acne. But it doesn’t respond to the same treatments. Antibiotics or harsh skincare products may even make it worse.
What Causes Fungal Acne?

Several factors encourage fungal acne. Hot and humid weather creates the perfect conditions for yeast to grow. Wearing tight or sweaty clothes for too long can also trigger it. Using heavy or oily skincare products clogs pores and feeds the yeast.
Sometimes, antibiotics cause fungal acne. These medications kill bacteria, but they also disrupt the skin’s balance. This allows yeast to take over. People living in tropical climates or sweating a lot during workouts are at a higher risk.
How Can Fungal Acne Be Treated?

Treating fungal acne requires targeting the yeast directly. Regular acne products do not work for this condition. Instead, antifungal treatments are needed. Here are the best approaches:
1. Antifungal Creams and Lotions
Over-the-counter antifungal creams are quite effective. Choose products that contain ketoconazole or clotrimazole. They work wonderfully to reduce yeast growth. Only apply to the affected areas.
2. Antifungal Shampoos
You can literally use antifungal shampoos as body washes. Ingredients like selenium sulfide and zinc pyrithione are helpful. Let them sit on your skin for a few minutes before rinsing off.
3. Oral Antifungal Medications
In severe cases, you need to visit a dermatologist and get the treatment. He or she might prescribe oral antifungal medication. These medicines eliminate yeast. A dermatologist should guide this treatment.
The Importance of Proper Skincare for Fungal Acne

Good skincare plays a big role in managing fungal acne. The right routine helps prevent flare-ups and keeps the skin healthy.
1. Cleanse Gently
A mild, non-oily cleanser should be used daily. This removes sweat and excess oil without irritating the skin.
2. Avoid Heavy Products
Heavy creams and oils can worsen fungal acne. Lightweight, water-based moisturizers are better choices.
3. Use Antifungal Products Regularly
Even after fungal acne clears, occasional use of antifungal products can prevent its return. This is especially useful in humid climates.
4. Choose Breathable Clothing
Loose, breathable fabrics like cotton are recommended. These reduce sweat buildup and irritation.
Can Natural Remedies Help?

Some natural remedies may support fungal acne treatments. While they are not substitutes for medical care, they can be helpful additions.
1. Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil has antifungal properties. A few drops diluted in a carrier oil can be applied to the skin. It should be used sparingly to avoid irritation.
2. Apple Cider Vinegar
Diluted apple cider vinegar balances the skin’s pH. This discourages yeast growth. It can be applied with a cotton pad or used as a toner.
3. Sulfur Soaps
Sulfur has antifungal benefits. Soaps with sulfur help cleanse the skin and reduce yeast. These are affordable and widely available.
Preventing Fungal Acne
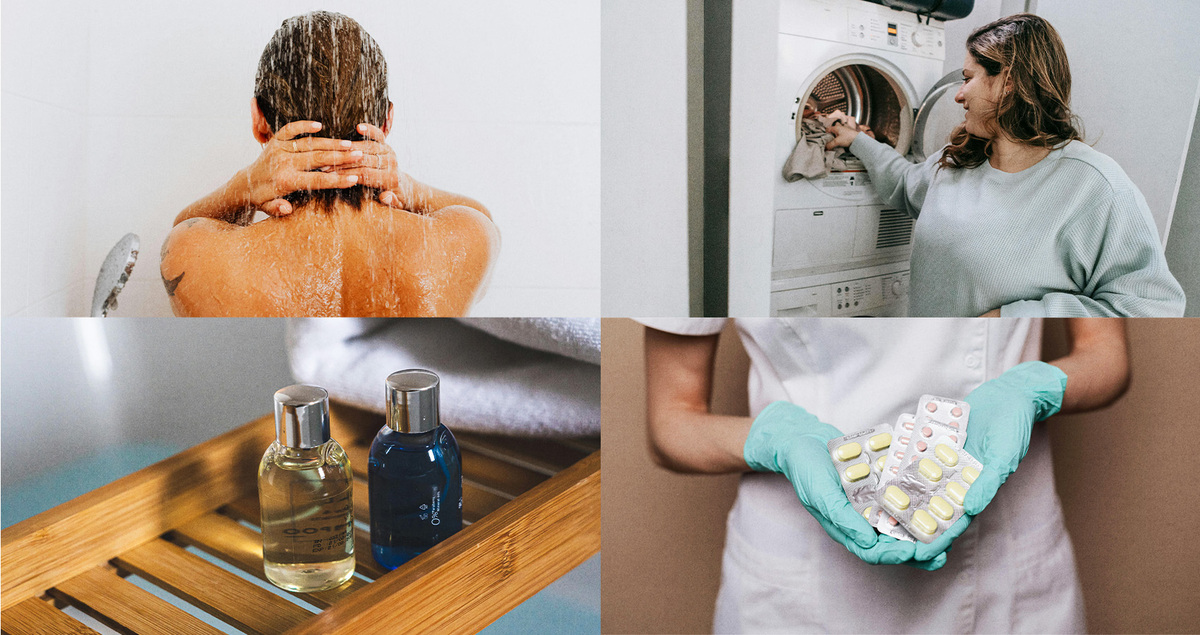

Preventive steps can reduce the risk of fungal acne. Making small changes to daily habits often helps.
1. Shower After Sweating
Sweat is a major trigger for fungal acne. Showering immediately after exercise removes sweat and yeast from the skin.
2. Wash Clothing Regularly
Sweaty clothes should not be worn for long periods. Workout gear and undergarments should be washed after each use.
3. Use Antifungal Shampoos
Occasionally using antifungal shampoos as body washes can prevent yeast from overgrowing. This is especially helpful during hot seasons.
4. Avoid Overusing Antibiotics
Antibiotics should only be used when necessary. Overuse can disrupt the skin’s balance, leading to fungal acne.
FAQs About Fungal Acne
1. How Can Fungal Acne Be Identified?
Fungal acne looks like small, uniform bumps. These are often itchy and occur on areas like the chest and back. Regular acne treatments may not work, which is a sign it could be fungal acne.
2. Can Fungal Acne Spread to Others?
No, fungal acne is not contagious. It is caused by an imbalance in the skin’s natural yeast, not by bacteria or viruses.
3. How Long Does Treatment Take?
With proper treatment, fungal acne usually improves in two to four weeks. Severe cases may take longer to fully clear.
4. Are Home Remedies Enough?
Home remedies can help, but they are not enough on their own. Medical treatments, like antifungal creams and shampoos, are more effective.
5. Should a Dermatologist Be Consulted?
Yes, a dermatologist should be consulted if fungal acne does not improve with home care. They can provide stronger treatments and confirm the diagnosis.
The Difference Between Fungal Acne and Regular Acne
Understanding the difference is key to finding the right treatment. Regular acne is caused by bacteria and clogged pores. It often includes blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts. Fungal acne, on the other hand, is caused by yeast. It appears as small, itchy bumps and does not form blackheads or cysts.
Regular acne treatments, like benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, do not work on fungal acne. These can even make the condition worse. Antifungal products are the best solution.
Why Early Treatment is Important
Ignoring fungal acne can make the problem worse. The condition can spread if not treated properly. This may cause discomfort and damage the skin’s appearance.
Early treatment helps control the yeast and prevent long-term issues. Sticking to a proper routine ensures the skin heals faster and stays healthy.
When to See a Dermatologist
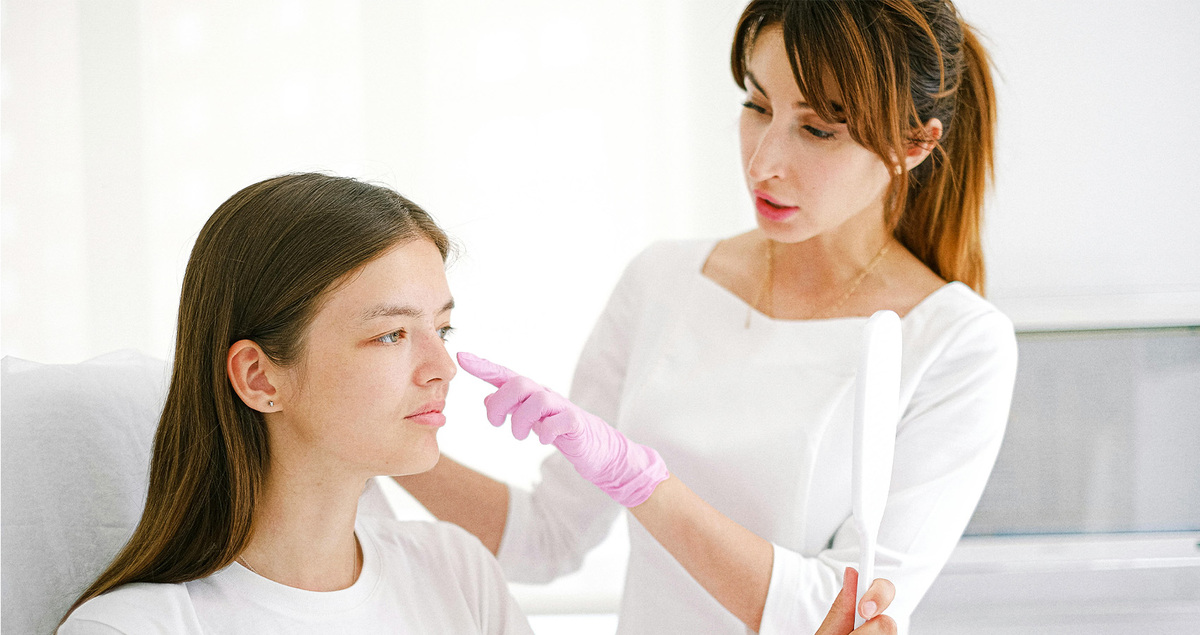

If fungal acne does not improve, a dermatologist should be consulted. They can confirm whether the issue is fungal acne or another condition. Prescription medications or stronger topical treatments may be needed.
A dermatologist can also provide advice on preventing future flare-ups. This ensures better long-term results.
Conclusion
Fungal acne can be challenging, but it is treatable. Understanding its causes and symptoms makes it easier to manage. The right treatments for fungal acne include antifungal products, good skincare habits, and preventive steps.
Natural remedies can support medical treatments, but professional help is recommended for severe cases. Early action leads to faster results and clearer skin. With proper care, fungal acne can be controlled, and healthy skin can be maintained.










