How Can Botox Help with Medical Conditions Such as Migraine: Understanding its Therapeutic Benefits
Botox: A trusted solution for chronic migraine relief.
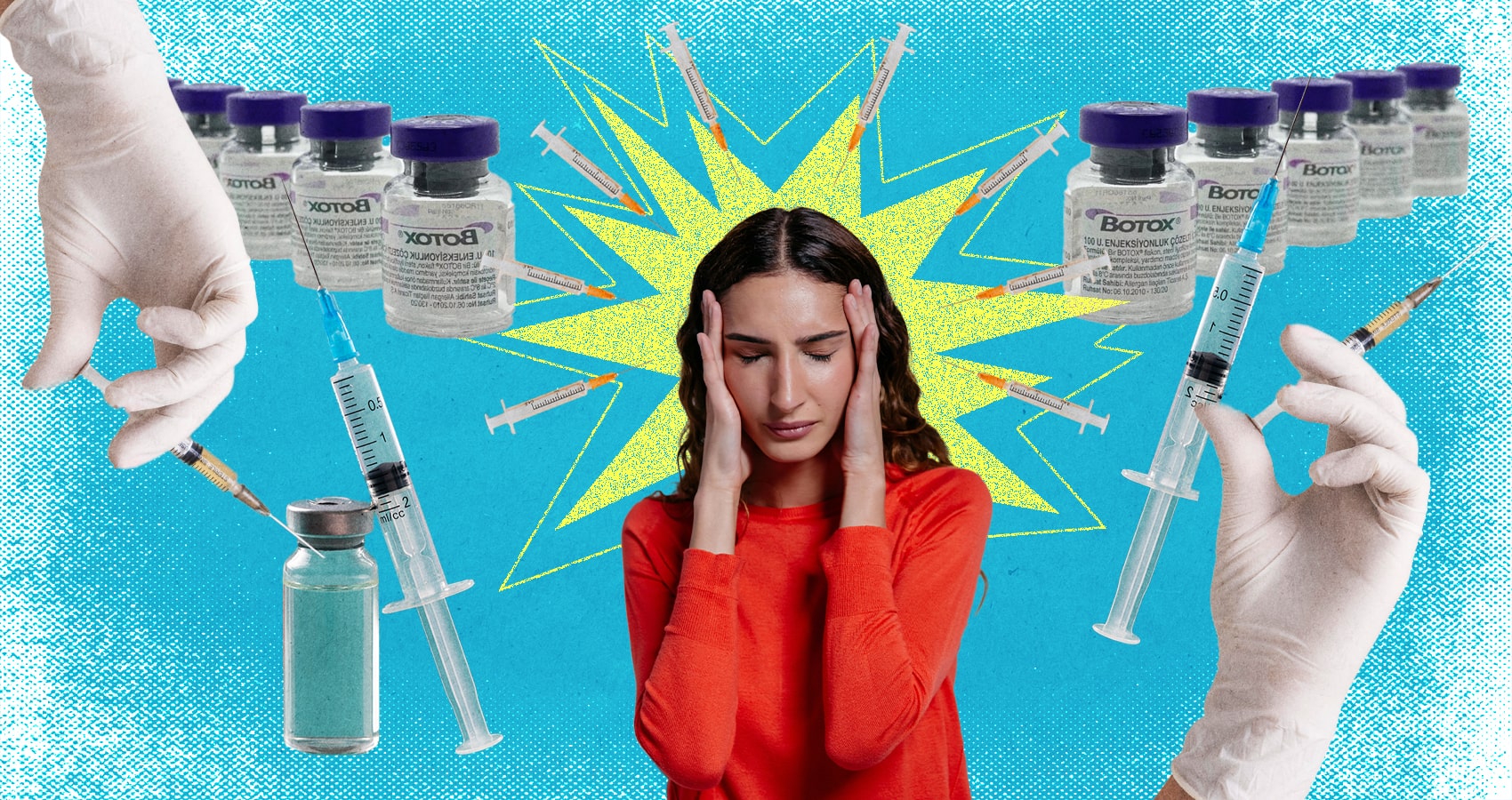
Botox has become more than just a cosmetic treatment; it plays a significant role in managing medical conditions like migraines. By temporarily paralyzing certain muscles, Botox can reduce the frequency and severity of migraines, providing relief for those who suffer from this debilitating condition. This treatment involves injecting the compound into specific areas like the forehead and neck, blocking pain signals to the brain.
If you're considering Botox for migraines, finding the best Botox clinic for this treatment can make a difference in your experience and results. It's important to choose a provider experienced in administering Botox for medical purposes, not just aesthetics. For various treatments, including Botox, you can explore options professionals recommend. This guarantees you receive the right care tailored to your needs.
While Botox isn't a cure for migraines, it has been FDA-approved for reducing the number of headache days in chronic sufferers. It's just one of many treatment options available, but it has helped many people regain a sense of normalcy in their daily lives. Understanding how this option works and what you can expect might be your first step toward finding relief.
Understanding Botox and Its Mechanism of Action
Botox is commonly associated with cosmetic procedures, yet it has significant medical uses. These include treating migraine headaches and other conditions by targeting neuromuscular activities.
Botox: What It Is and Its Medical Applications

Botox is derived from botulinum toxin, a neurotoxic protein. It is used not only for cosmetic purposes but also for medical treatments. You might find it effective for managing chronic migraine, cervical dystonia, and excessive sweating. For migraines, Botox is injected into specific muscles, which can help in reducing headache frequency and severity. These treatments are FDA-approved and widely accepted in the medical community. The process typically involves several small injections in areas like the forehead and neck.
The Biological Mechanism Behind Botox for Migraines
Botox works by blocking chemicals that carry pain signals, such as acetylcholine, from nerves to muscles. This leads to muscle relaxation and a decrease in migraine symptoms. Research shows that when Botox is injected, it prevents the release of specific neurotransmitters involved in pain transmission. This reduces muscle contractions and dulls the sensation of pain. By targeting these pathways, Meamo botox not only reduces frequency but also helps in managing the intensity of migraines. The benefits usually appear within a few weeks after treatment.
Botox in the Treatment of Migraines

Botox is used to reduce the frequency and severity of chronic migraines by targeting specific areas in the head and neck. It is known for offering relief for those who suffer from headaches repeatedly each month.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Botox for Migraine Relief
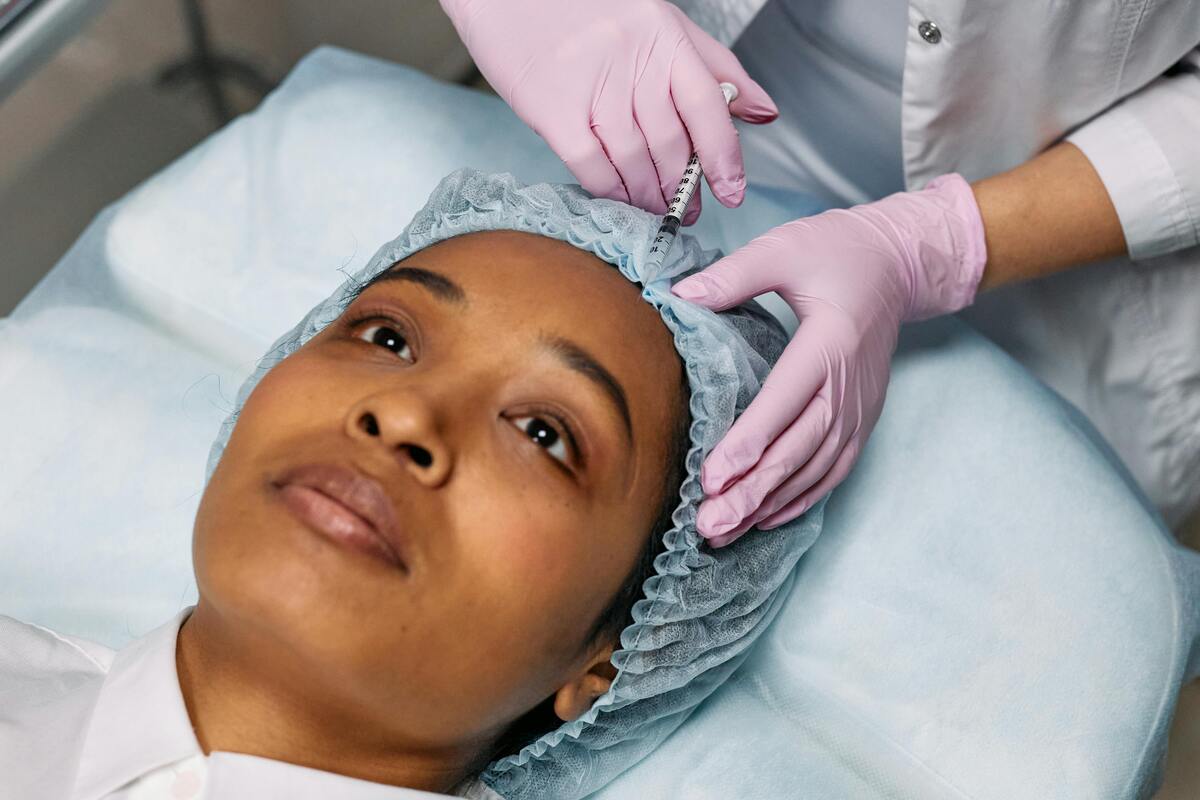
Botox, or OnabotulinumtoxinA, is a recognized treatment for migraines. Studies show it reduces the number of headache days experienced by those with chronic migraines. It is particularly beneficial for people who suffer from 15 or more headaches days a month. Patients may not notice immediate changes, and it might take several weeks to see results.
Research indicates Botox can alleviate different types of migraines, such as chronic and episodic. It works by blocking the release of chemicals that transmit pain signals in the brain. Providing relief for many, it has become a preferred option for long-term migraine management.
Procedure: Administration of Botox for Migraine
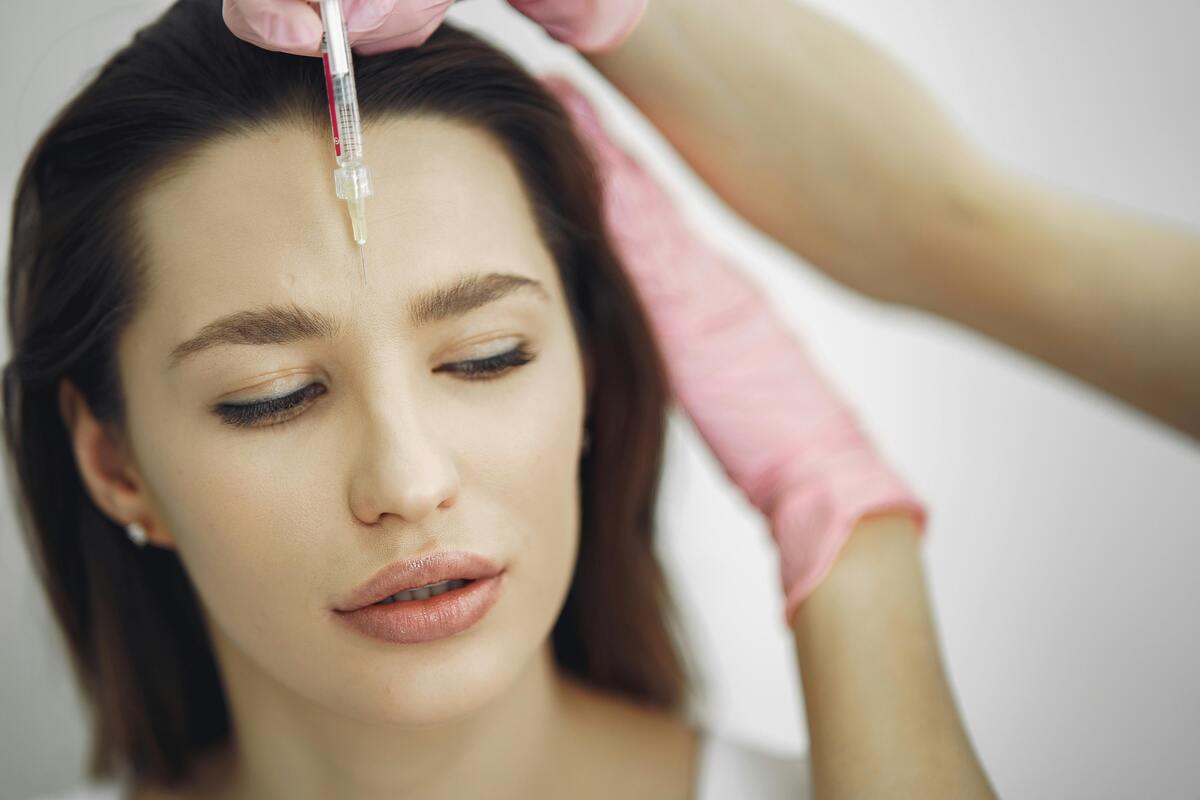

When you receive Botox for migraines, the treatment involves a series of injections. Doctors target muscles in areas like the forehead, neck, and shoulders to administer the injections. The process usually takes about 15 minutes and involves multiple small injections.
It’s important to follow specific guidelines during such treatments. For instance, you should avoid lying down for an hour after an injection. Additionally, it’s advised not to massage injection sites for 24 hours to prevent spreading Botox beyond the intended area.
Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Botox Treatments

Many patients report fewer and less intense migraines after receiving Botox treatments. The therapy is generally well-tolerated, with side effects like mild pain at injection sites. The exact mechanism of how Botox prevents headaches is not wholly understood, adding to its unique nature.
The safety profile of Botox is favorable for many users. However, discussing potential risks with a healthcare provider is important to guarantee it is suitable for your specific needs. Regular follow-up appointments help assess the treatment's effectiveness and adjust the approach if necessary.
Conclusion
Botox offers promising results for those suffering from migraines. By reducing the frequency and severity of migraine attacks, it provides relief to many people.
Benefits of Botox for Migraines:
- Less frequent headaches
- Reduced pain intensity
- Improved daily functioning
Unlike traditional pain relief methods, Botox targets the underlying mechanisms of migraines. It deals with both motor and sensory systems, helping to manage chronic issues.
If you are considering this treatment, consult a healthcare professional to know if it’s the right option for you.
Visit Urban Aesthetics for the best botox treatment in Gilbert, Arizona.











